快速查题-ACCA英国注册会计师试题
- 不限题型
- 不定项选择题
- 单选题
- 填空题
- 材料题
- 简答题
- 论述题
Which two of the following costs are likely to rise when just in time (JIT) manufacturing is introduced?
Which of the following could be used to describe activity based budgeting (ABB)?
Select all that apply.
Ohno Co uses activity based costing and produces three products called EM, TM and GM.
Ohno Co expects to incur the following indirect production costs next year.
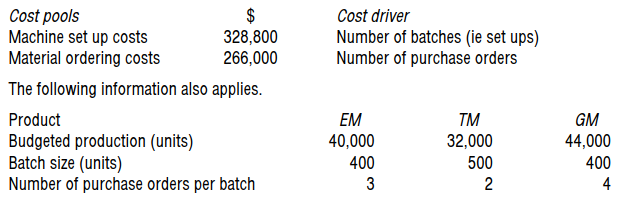
What is the cost per machine set-up?
Ohyes Co uses activity based costing and produces three products called ET, TT and GT.
Ohyes Co expects to incur the following indirect production costs next year.
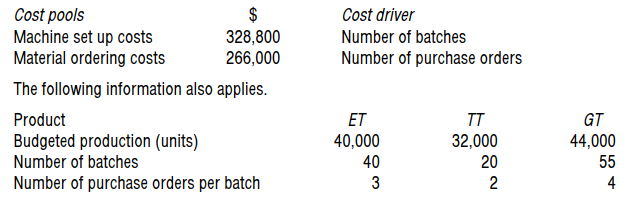
What is the cost per purchase order?
Product YZ2 is made in a production process where machine time is a bottleneck resource. Production of one unit of Product YZ2 takes 0.25 machine hours. The costs and selling price of Product YZ2 are as follows:

In a system of throughput accounting, what is the return per factory hour?
A company manufactures Product Q, which sells for $50 per unit and has a material cost of $14 per unit and a direct labour cost of $10 per unit. The total direct labour budget for the year is 18,000 hours of labour time at a cost of $10 per hour. Factory overheads are $1,620,000 per year. The company has identified machine time as the bottleneck in production. Product Q needs 0.05 hours of machine time per unit produced. The maximum capacity for machine time is 6,000 hours per year.
What is the throughput accounting ratio for Product Q (to 1 dp)?
Which two of the following statements about activity based costing are true?
Which two of the following statements about activity based costing are true?
ABC is felt to give a more useful product cost than classic absorption costing (with overheads absorbed on labour hours) if which of the following two apply?
Calculate the overhead cost of centre hire which would be allocated to an auditing course under activity based costing to the nearest dollar.


